Misc 10 Find sin 𝑥/2, cos 𝑥/2 and tan 𝑥/2 for sin𝑥 = 1/4 , 𝑥 in quadrant II Given that x is in quadrant II So, 90° < x < 180° Replacing x with 𝑥/2 (90°)/2 < 𝑥/2 < (180°)/2 45° < 𝑥/2 < 90° So, 𝑥/2 lies in Ist quadrant In Ist quadrant, sin , cos & tan are positive sin 𝑥/2 ,Tan a=4/3, condition pi/2 Cos b = 1/2, condition 0 Need exact value cos(ab) Sin(ab) Tan(ab) I believe a would be in quadrant 2 where x is negative and y is positiveTrigonometry Find the Other Trig Values in Quadrant I cos (s)=3/4 cos (s) = 3 4 cos ( s) = 3 4 Use the definition of cosine to find the known sides of the unit circle right triangle The quadrant determines the sign on each of the values cos(s) = adjacent hypotenuse cos (
Find Sin X 2 Cos X 2 And Tan X 2 If Tan X 4 3 X In Quadrant Ii Sarthaks Econnect Largest Online Education Community
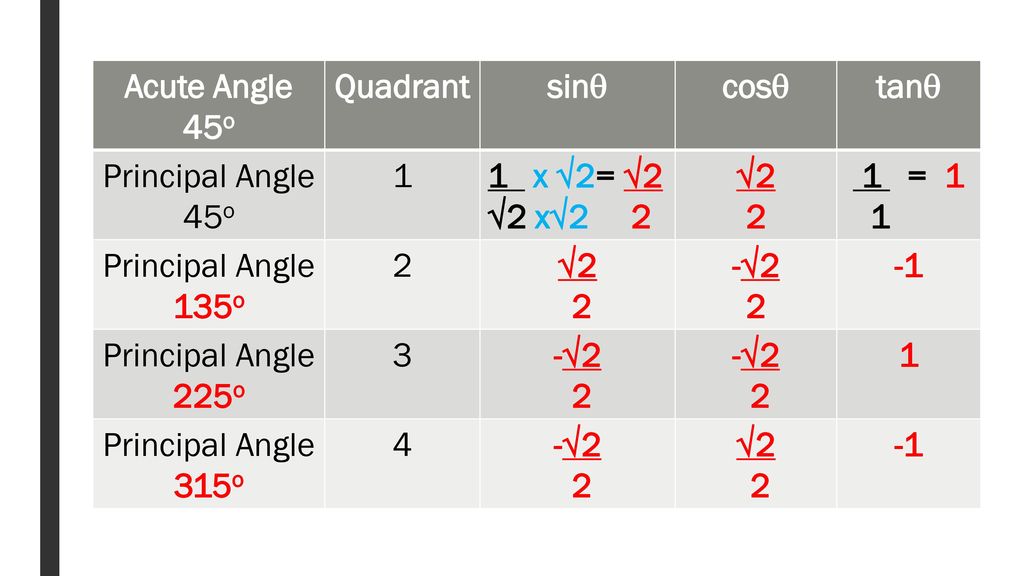
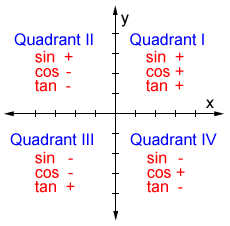
Quadrant 1 2 3 4 sin cos tan
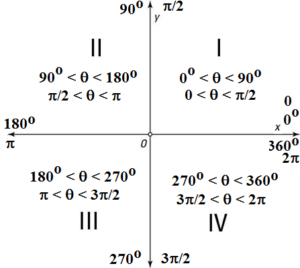
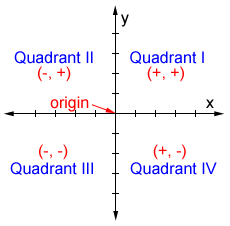
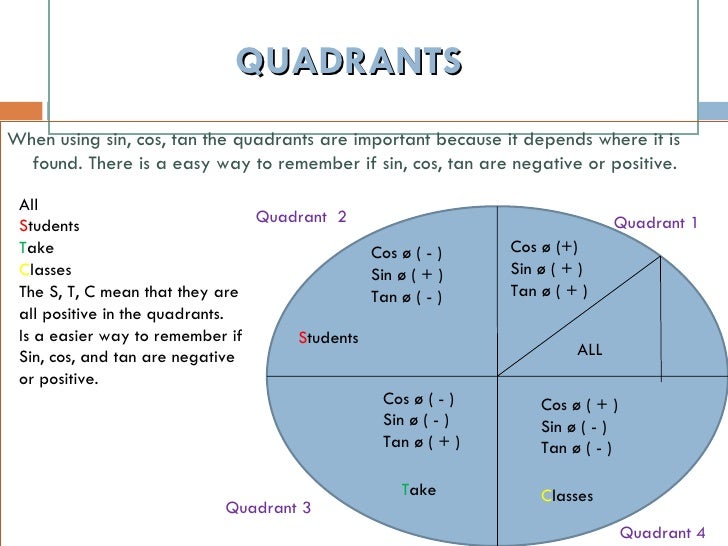
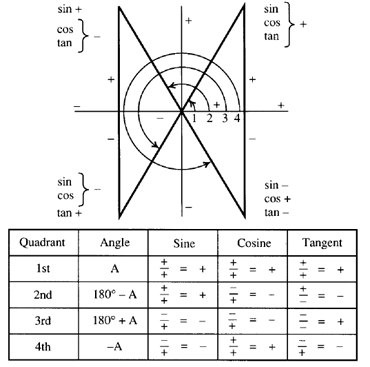
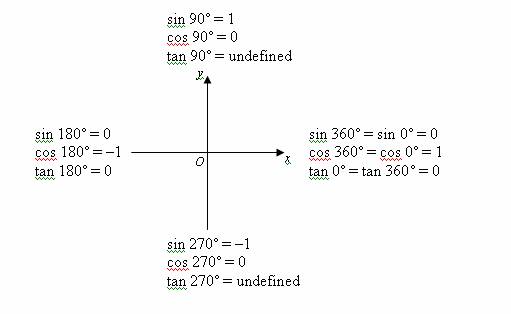
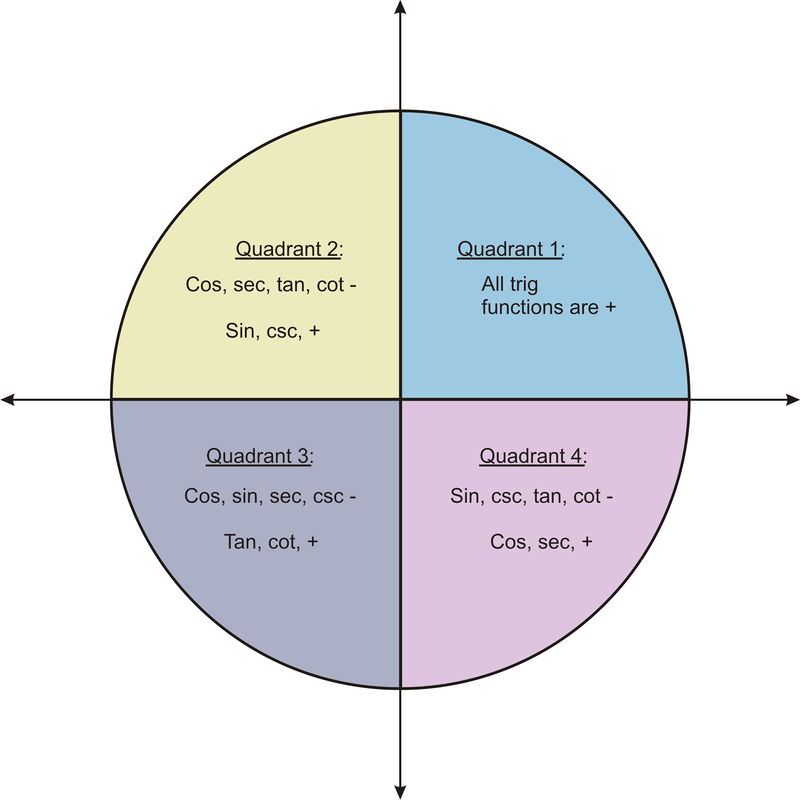
Quadrant 1 2 3 4 sin cos tan-The graph of cos the same as the graph of sin though it is shifted 90° to the right/ left For this reason sinx = cos (90 x) and cosx = sin (90 x) Note that cos is an even function it is symmetrical in the yaxis sin is an odd function The graph of tan has asymptotes Summary First Quadrant All are positive in this quadrant Second Quadrant Only sin is positive in this quadrant Third Quadrant Only tan is positive in this quadrant Fourth Quadrant Only cos is positive in this quadrant We now consider angles in cartesian plane We divide the plane into four quadrants in the anticlockwise sense as shown




Sine Cosine And Tangent In The Four Quadrants Teachablemath
You can put this solution on YOUR website!Cosine cos (210°) = −1732 / 2 = −0866 Tangent tan (210°) = −1 / −1732 = 0577 Note Tangent is positive because dividing a negative by a negative gives a positive In Quadrant IV, sine and tangent are negative Since $\cos^2t\sin^2t=1$, dividing both sides by $\cos^2 t$ we also have $$1\tan^2t=\frac 1{\cos^2t}$$ Also, in the second quadrant, $\cos t0$ Use the second equation and the restriction to find $\cos t$, then use the first equation and the restriction to find $\sin t$ Then add those for your final answer
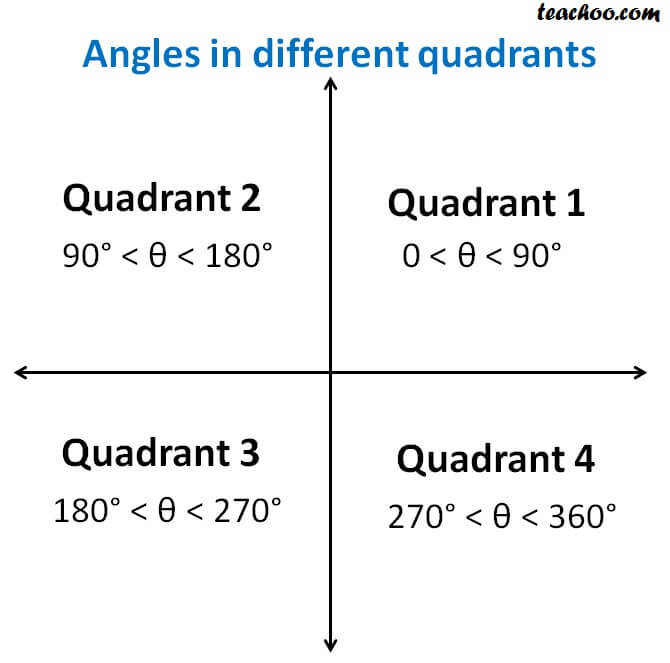
⇒ cos A = cos 2 4 0 0 ⇒ A = 2 4 0 0 Now, c o s B = − 2 1 ⇒ c o s B = − cos 6 0 0 when B does not lie in the third quadrant ⇒ c o s B = cos (1 8 0 0 − 6 0 0) ⇒ c o s B = cos 1 2 0 0 ⇒ B = 1 2 0 0 Substituting the value of A and B in equation (1) and we get, tan 1 2 0 0 sin 2 4 0 0 4 sin 1 2 0 0 − 3 tan 2 4 0 0 ⇒ tan (1When angle a is in Quadrant 3 (between 180° and 270°), both the adjacent and the opposite side are negative Hence, Sine and Cosine are negative and since Tangent (T) is a division between two negative numbers, it is the only trigonometric function that is positive Sine, Cosine and Tangent in Quadrant 4 Transcript Let s see the angles in different Quadrants In Quadrant 1, angles are from 0 to 90 In Quadrant 2, angles are from 90 to 180 In Quadrant 3, angles are from 180 to 270 In Quadrant 4, angles are from 270 to 360 To learn sign of sin, cos, tan in different quadrants, we remember Add Sugar To Coffee Representing as a table Quadrant I Quadrant II Quadrant III Quadrant IV sin cos tan
We know that sin^2 a cos^2 a= 1 ==> cos^2 a = 1 sin^2 a ==> cos^2 a = 1 (2/3)^2 ==> cos^2 a = 1 4/9 ==> cos^2 a= 5/9 ==> cos a = sqrt5/3 But a is in the 2nd quadrant where cos a iaQuestion Find the exact value, given that cos A= 1/3, with A in quadrant I, and sin B= 1/2, with B in quadrant IV, and sin C= 1/4, with C in quadrant II sin(AB) I don't understand this problem Why do they give sin C? 1 Answer Dean R tanθ = 3 4 means an opposite of 3, an adjacent of 4, so a hypotenuse of 5, because 32 42 = 52 cosθ = adjacent hypotenuse = ± 4 5
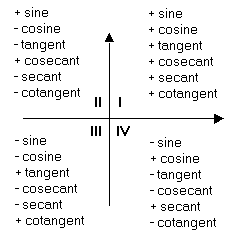



What Trig Functions Are Negative In Quadrant 2 Socratic



5 Signs Of The Trigonometric Functions
Please help me Found 2 solutions by lwsshak3, jim_thompson5910If Tan Theta 3 4 And Theta Is Not In First Quadrant Then Sin Pi 2 Theta Cot Pi Theta YoutubeFind the Other Trig Values in Quadrant I csc (x)=4 csc(x) = 4 csc ( x) = 4 Use the definition of cosecant to find the known sides of the unit circle right triangle The quadrant determines the sign on each of the values csc(x) = hypotenuse opposite csc ( x) = hypotenuse opposite




完了しました Quadrant 1 2 3 4 Sin Cos Tan Quadrant 1 2 3 4 Sin Cos Tan Gambarsaeawp




Section 4 4 Trigonometric Functions Of Any Angle Ppt Download
A) quadrant 2 or 3 b) Quadrant 2 sin , cos , tan Quadrant 3 sin , cos , tan c) 115°, 245° 13 14 Answers may vary For example, given P (x, y) on the terminal arm of angle , sin , cos , and tan 15 a) 25°, 155°, 5°, 335° b) 148°, 352 o c) 16°, 106 o, 196 o, 286 o 16 a) could lie in quadrant 3 or 4 5 233° or 307° b) could lie Now Use the formula cos(A− B) = cosAcosB sinAsinB to evaluate Note that A = tan−1( 4 3) and B = sin−1( 12 13) Therefore, cos(tan−1(4 3) − sin−1( 12 13)) = cos(tan−1(4 3))cos(sin−1( 12 13)) sin(tan−1( 4 3))sin(sin−1(12 13)) = cosAcosB sinAsinB > Use triangles A and B to find the ratios = 3 5 ⋅ 5 13 4 5 ⋅ 12 13Answer (1 of 7) Here, tan x = 1/2 We know that, the relation between tan x and sec x is sec^2xtan^2x=1 Using this relation, first, we will determine the value of cos x and then, we will determine the value of sin x So now, sec^2xtan^2x=1 => sec^2x(1/4)=1 => sec^2x=1(1/4) => sec^2x=



Trigonometry Quadrant Formulas




Domain And Range Of Trigonometric Functions Videos Solved Examples
Free trigonometry calculator calculate trignometric equations, prove identities and evaluate functions stepbystep




14 1 Trigonometry




Trigonometric Ratios Iitutor




Sine Cosine And Tangent In The Four Quadrants Teachablemath



4 4 Trig Functions Of Any Angle Ppt Download




Lesson 41 Trigonometric Equations Ib Math Sl Santowski



Trigonometry




Pc12 Sol C06 Review
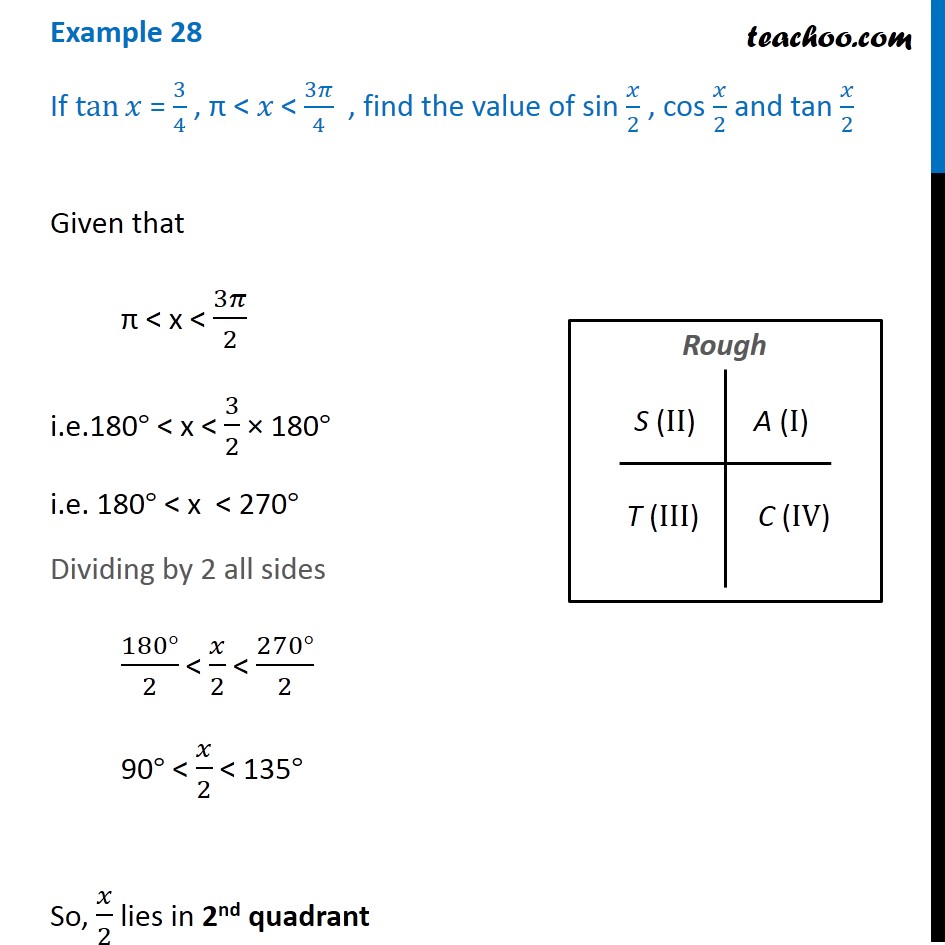



Example 28 If Tan X 3 4 Find Sin X 2 Cos X 2 Tan X 2



Relating Trigonometric Functions Trigonometry Socratic




Content The Four Quadrants



5 3 Trigonometric Ratios For Angles Greater Than 90o Ppt Download




Sine Cosine And Tangent In The Four Quadrants Teachablemath



Signs Of Trigonometric Ratios In Diffrent Quadrants Formed Due To Axes



Quadrant



Solved The Terminal Point P X Y Determined By A Real Number T Is Given Find Sin T Cos T And Tan T 1 2v 2 Sin T Cos T Tan T The Te Course Hero




If Cos X 2 12 13 And X Lies In Quadrant I Find The Values Of I Sin Youtube
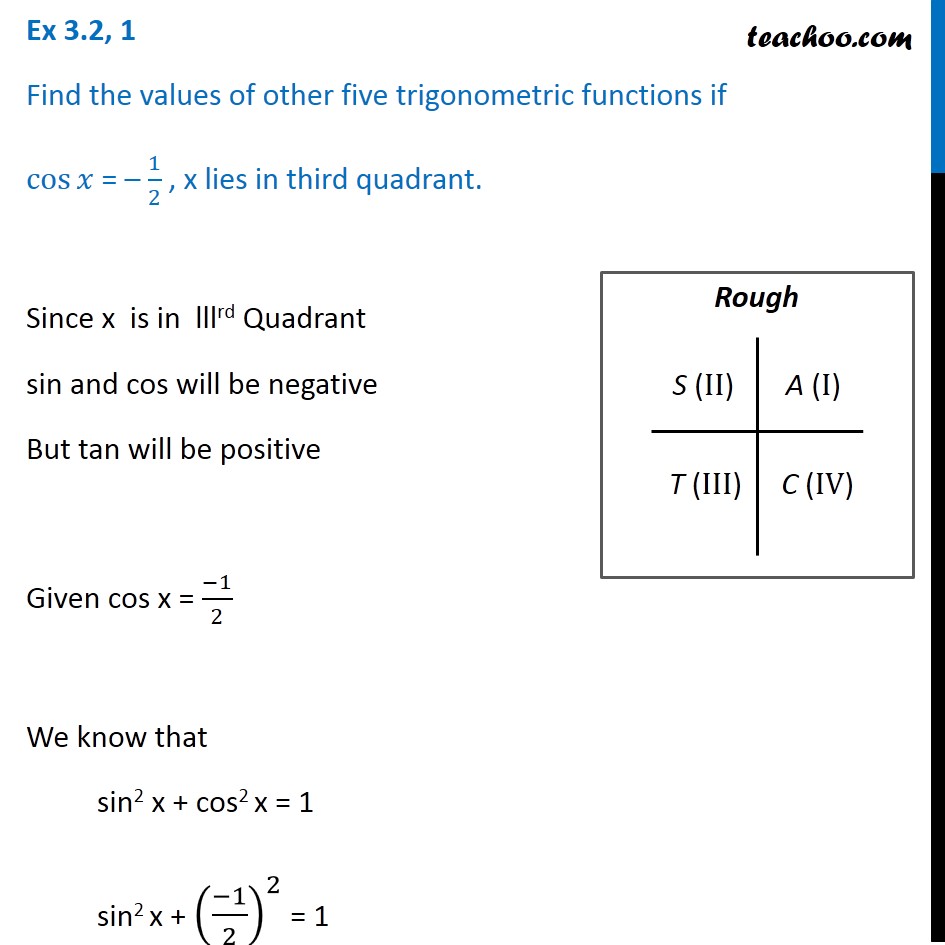



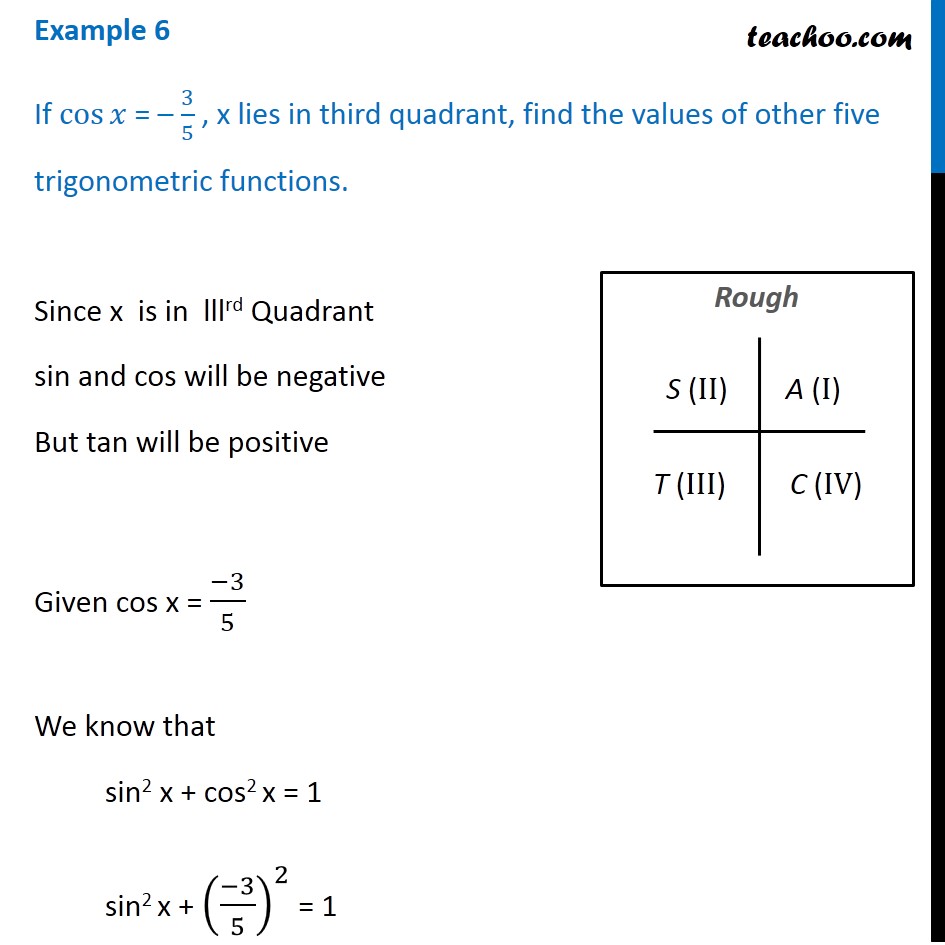
Ex 3 2 1 Find Values Of Other Five Trigonometric Functions If Cos X




The Trigonometry Functions



Trigonometry 1




完了しました Quadrant 1 2 3 4 Sin Cos Tan Quadrant 1 2 3 4 Sin Cos Tan Gambarsaeawp




Basic Trig Angle Mathematics Stack Exchange



Trigonometry Trigonometric Functions Functions In Quadrants Sparknotes



Trigonometric And Geometric Conversions Sin A B Sin A B Sin Ab




Ks 4 Mathematics S 4 Further Trigonometry 1



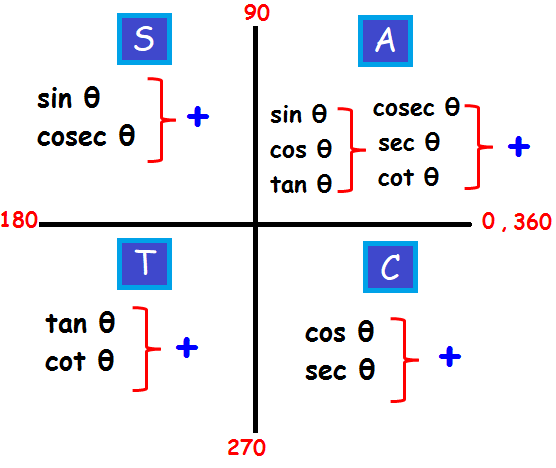
Cast Rule Mathonline




5 3 Trigonometric Ratios For Angles Greater Than 90o Ppt Download




Tv9jnwyyycco2m



Trigonometric Ratios Solutions Examples Videos



Trigonometric Table From 0 To 360 Cos Sin Cot Tan Sec Cosec



Trigonometry Angle Value Of Sinx Cosx Tanx In Quadrant 1 2 3 4 In Hindi Lecture 2 Youtube




Solved Let Sin X 2 3 With S In Quadrant Ii And Let Cos T Chegg Com



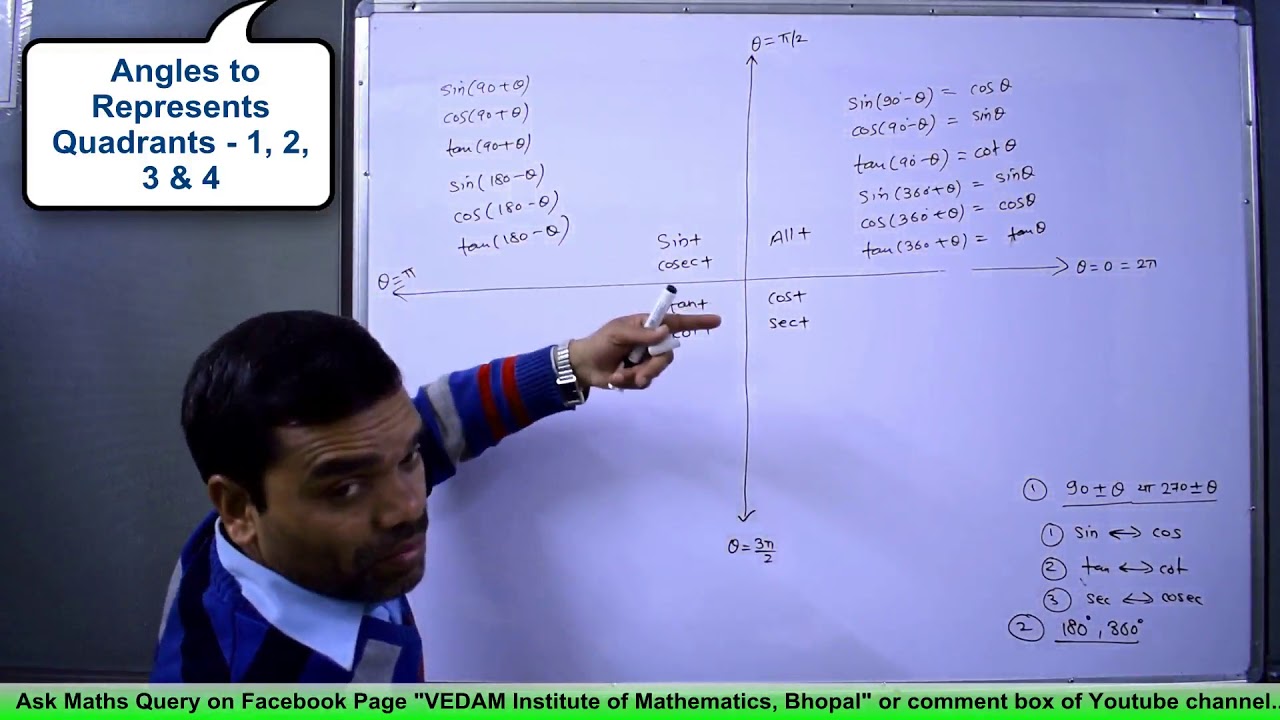
If Tan Theta 3 4 And Theta Is Not In First Quadrant Then Sin Pi 2 Theta Cot Pi Theta Youtube
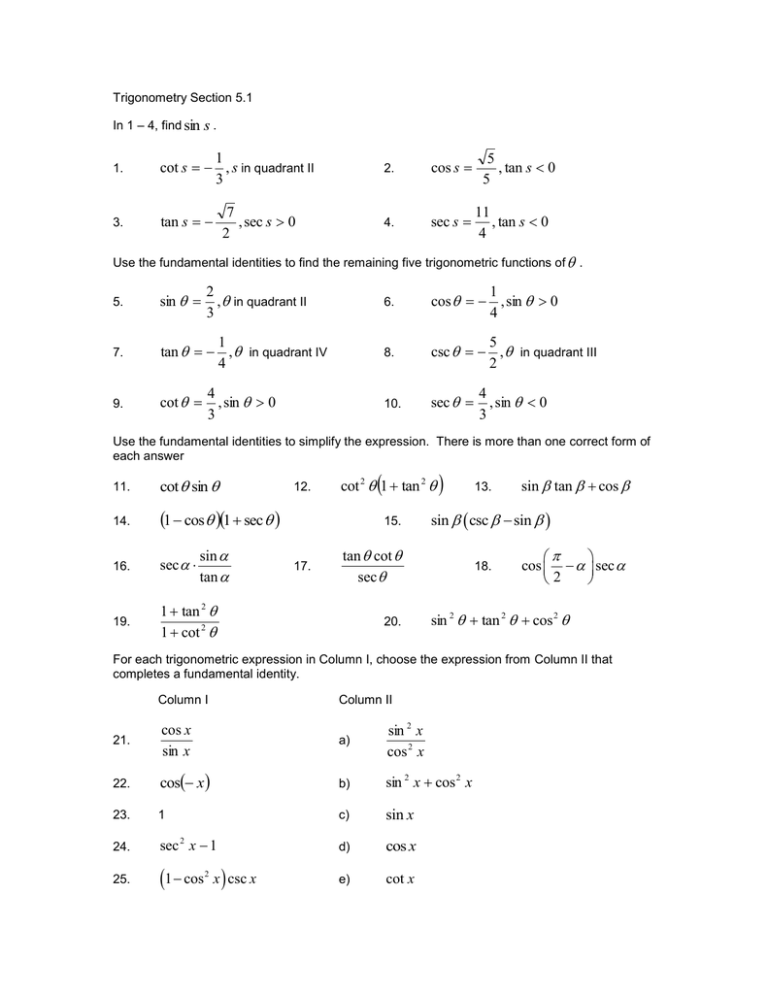



Trigonometry Section 5 1 In 1 4 Find 1 In Quadrant Ii 2 3 4 Use



Quadrant
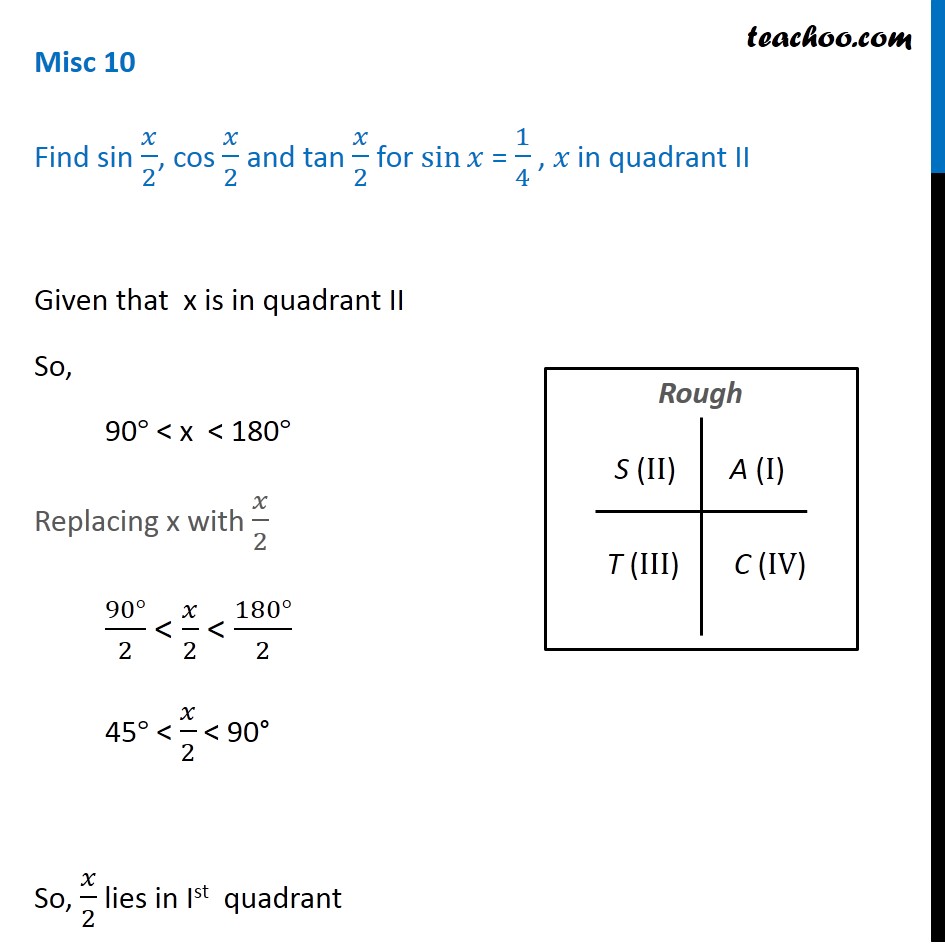



Misc 10 Sin X 1 4 Find Sin X 2 Cos X 2 Tan X 2 Chapter 3
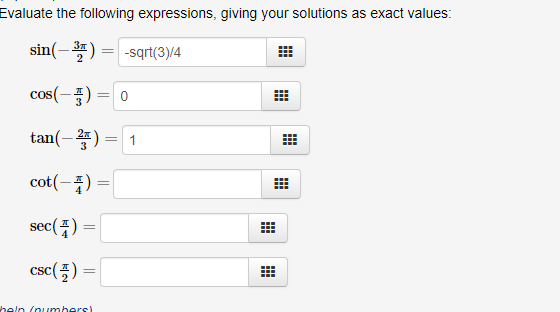



For Each Angle 0 Determine In Which Quadrant The Chegg Com




Cuadrante Geometria Wikipedia La Enciclopedia Libre



Find Sin X 2 Cos X 2 And Tan X 2 If Tan X 4 3 X In Quadrant Ii Sarthaks Econnect Largest Online Education Community
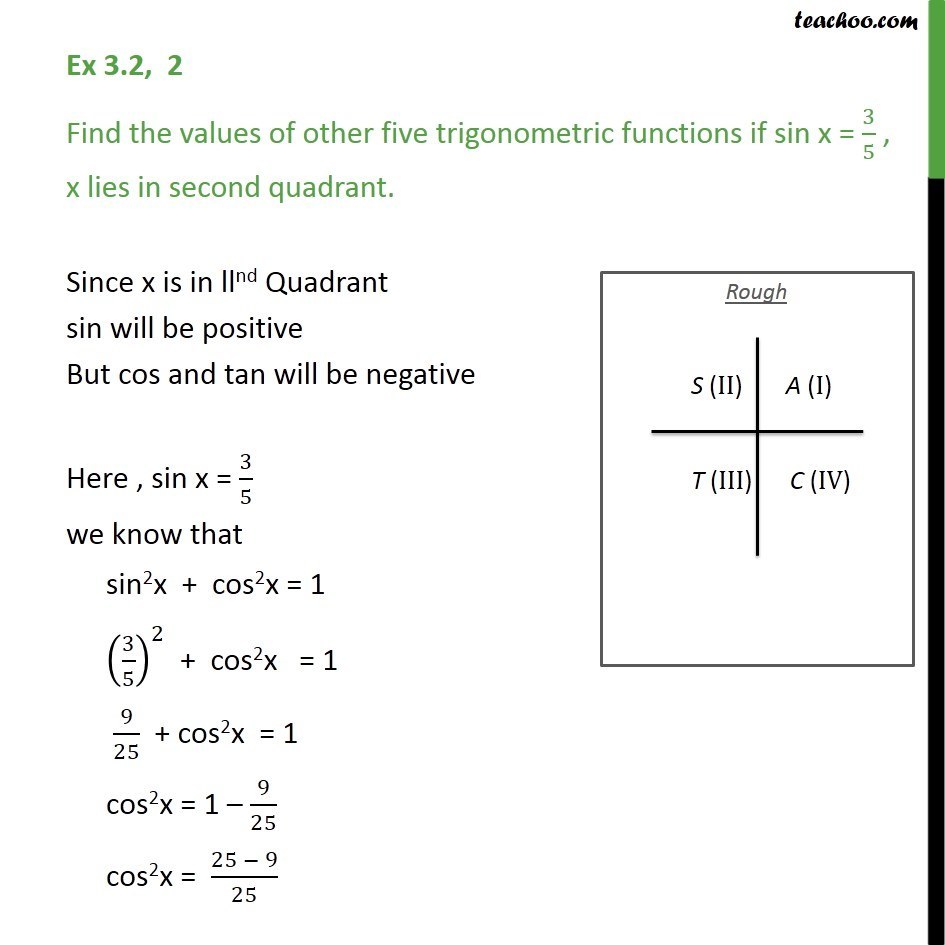



Ex 3 2 2 Find The Values Of Other Five Trigonometric Functions If S
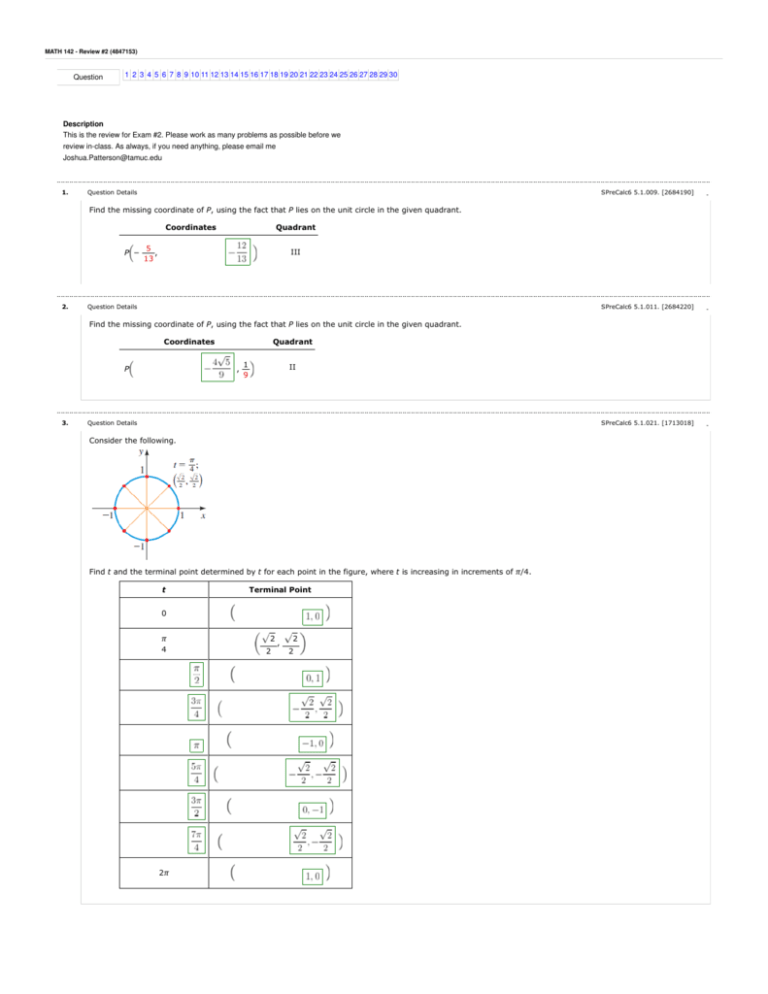



Exam 2 Review Key



Solved Find Sin 2x Cos 2x And Tan 2x If Cosx And X Chegg Com



Section 4 4 Reference Angles Precalculus



What Trig Functions Are Positive In Which Quadrants Socratic




1 9 3 4 1 3 3a 1 4b 1 1 4 1 3 2 3 B 6 4 3x 2 6 2 3 15 Manualzz



What Is All Students Take Calculus In Trig Studypug
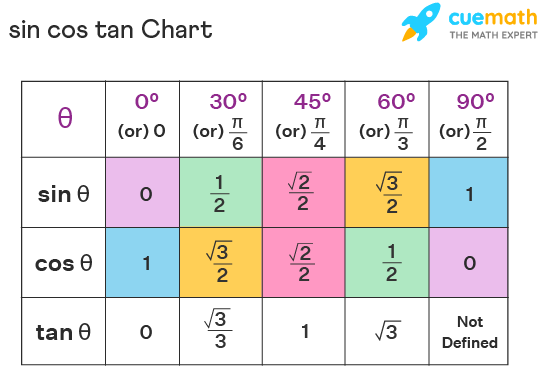



Sin Cos Tan Values Formulas Table Examples
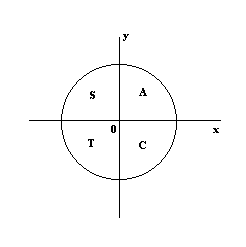



Sin Cos And Tan Mathematics A Level Revision




Content The Four Quadrants



If A And B Are Angles Of The First Quadrant Such That Tan A 3 4 And Tan B 1 7 Find The Quadrant In Which A B A B 2a And 3b Terminate Quora




Trigonometry




Coordinates 1 St Quadrant Y Axis 10 9
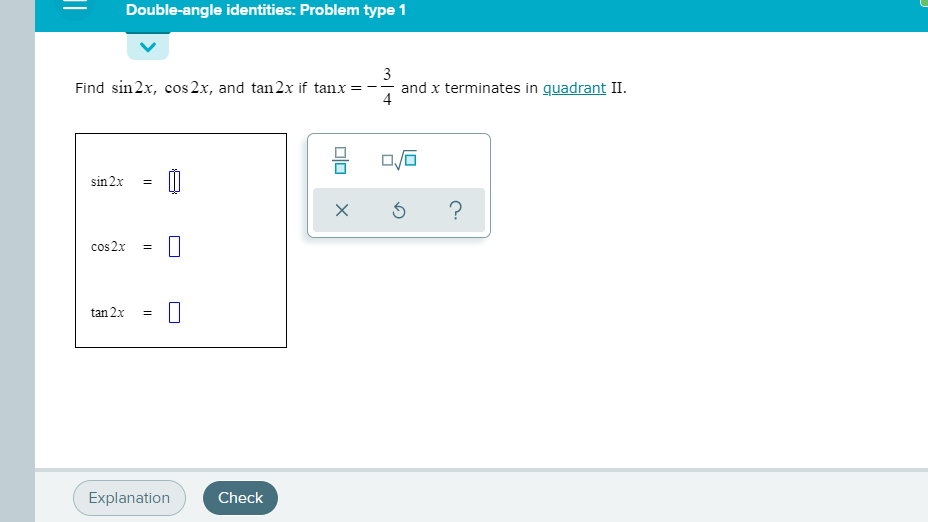



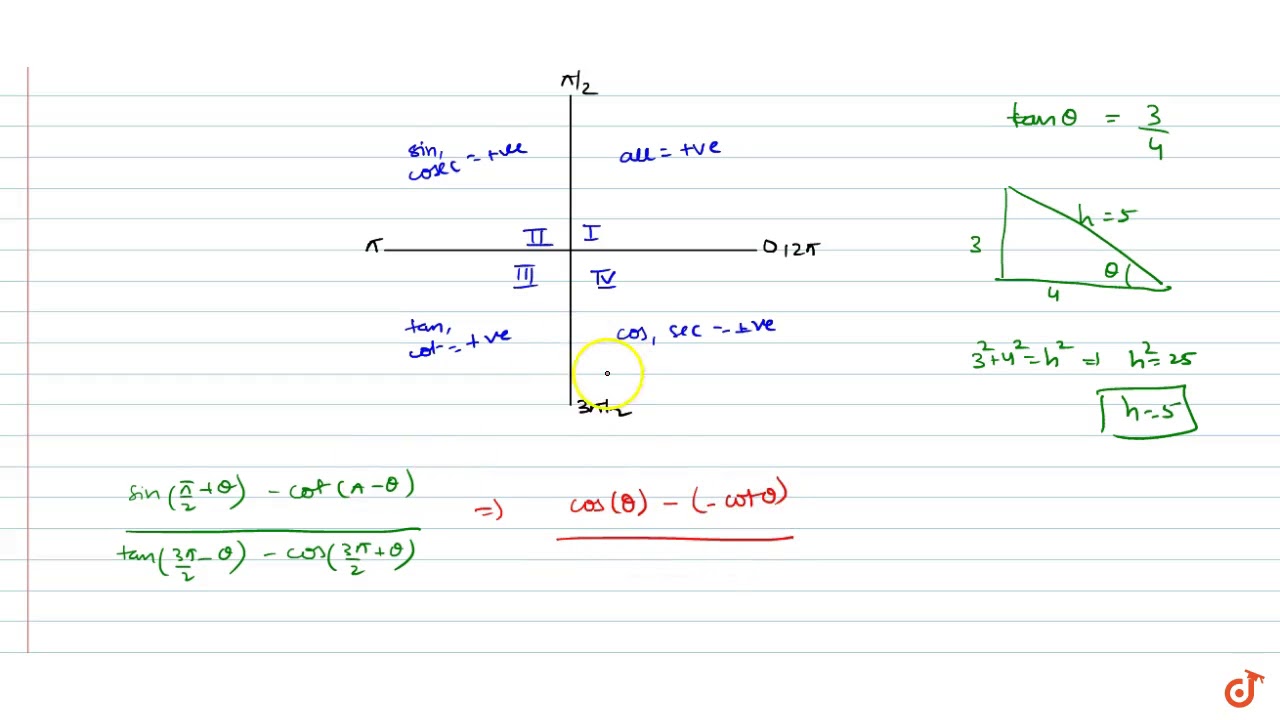
Solved Find Sin2x Cos2x And Tan2x If Tanx 3 4 And X Chegg Com




Determine The Quadrant When The Terminal Side Of The Angle Lies According To The Following Conditions Sin T 0 Tan T 0 Study Com
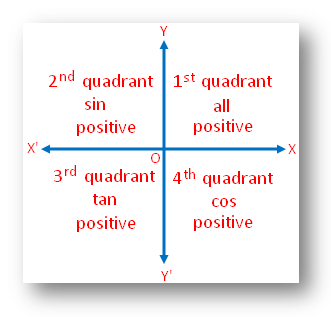



All Sin Tan Cos Rule Signs Of Trigonometrical Ratios Trigonometric Ratios




Sine Cosine And Tangent In Four Quadrants



Sin Cos Tan
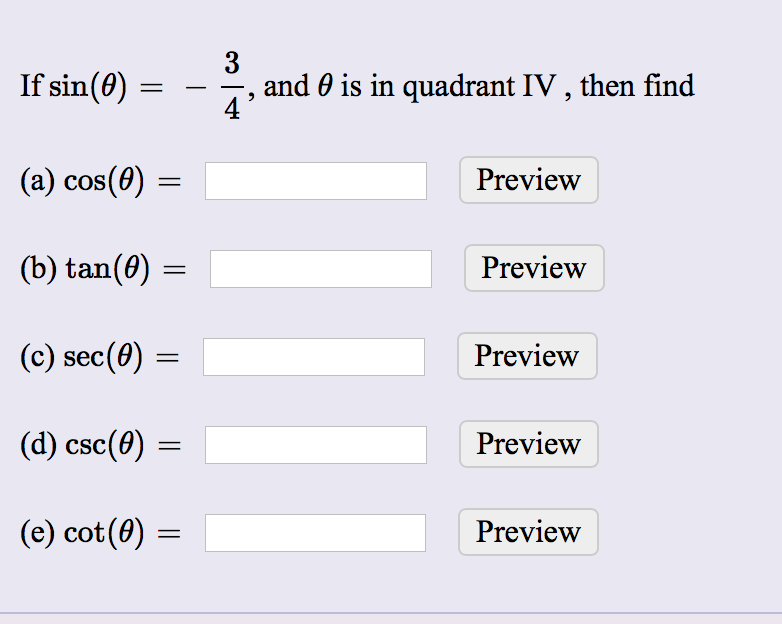



Solved If Sin Theta 3 4 And Theta Is In Quadrant Iv Chegg Com




Lesson 41 Trigonometric Equations Ib Math Sl Santowski




Trigonometry Quadrant Rule Solving Sin 8 Negative Value Examsolutions Youtube
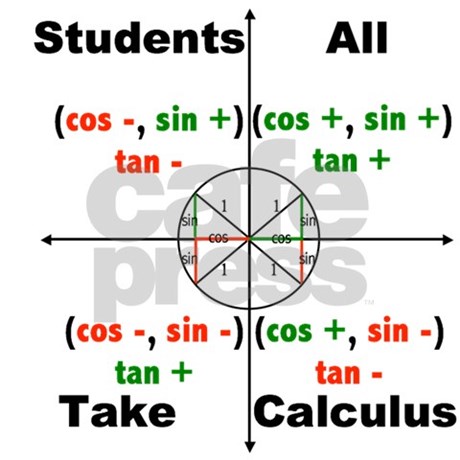



If Cos 0 And Sin 0 What Quadrant Is It In Socratic




A State The Sign Of Cos T In The Following Interval 3pi 2 2pi B State The Sign Of Cos T In The Following Interval Pi 2 Pi Study Com



1




The Trigonometry Functions




Trigonometry Sign For Sin Cos And Tan Quadrant I 0 90 Quadrant Ii 90 180 Quadrant Iii 180 270 Quadrant Iv 270 Ppt Download




The Unit Circle Reference Angles And Trigonometry Ppt Video Online Download
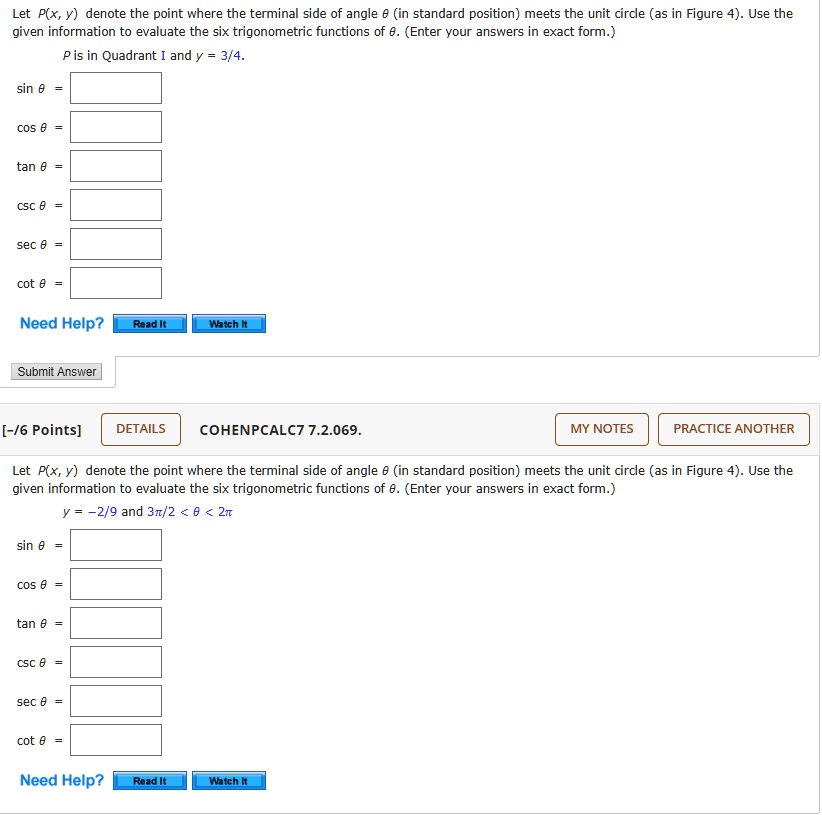



Solved Let P X Denote The Point Where The Terminal Side Of Angle In Standard Position Meets The Unit Circle As In Figure 4 Use The Given Information To Evaluate The Six Trigonometric




Content The Four Quadrants
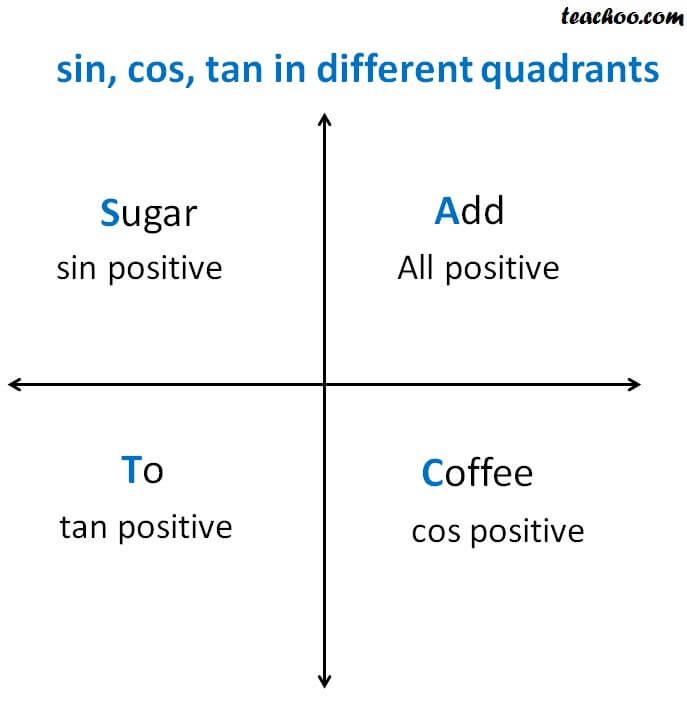



Signs Of Sin Cos Tan In Different Quadrants Finding Value Of Trign
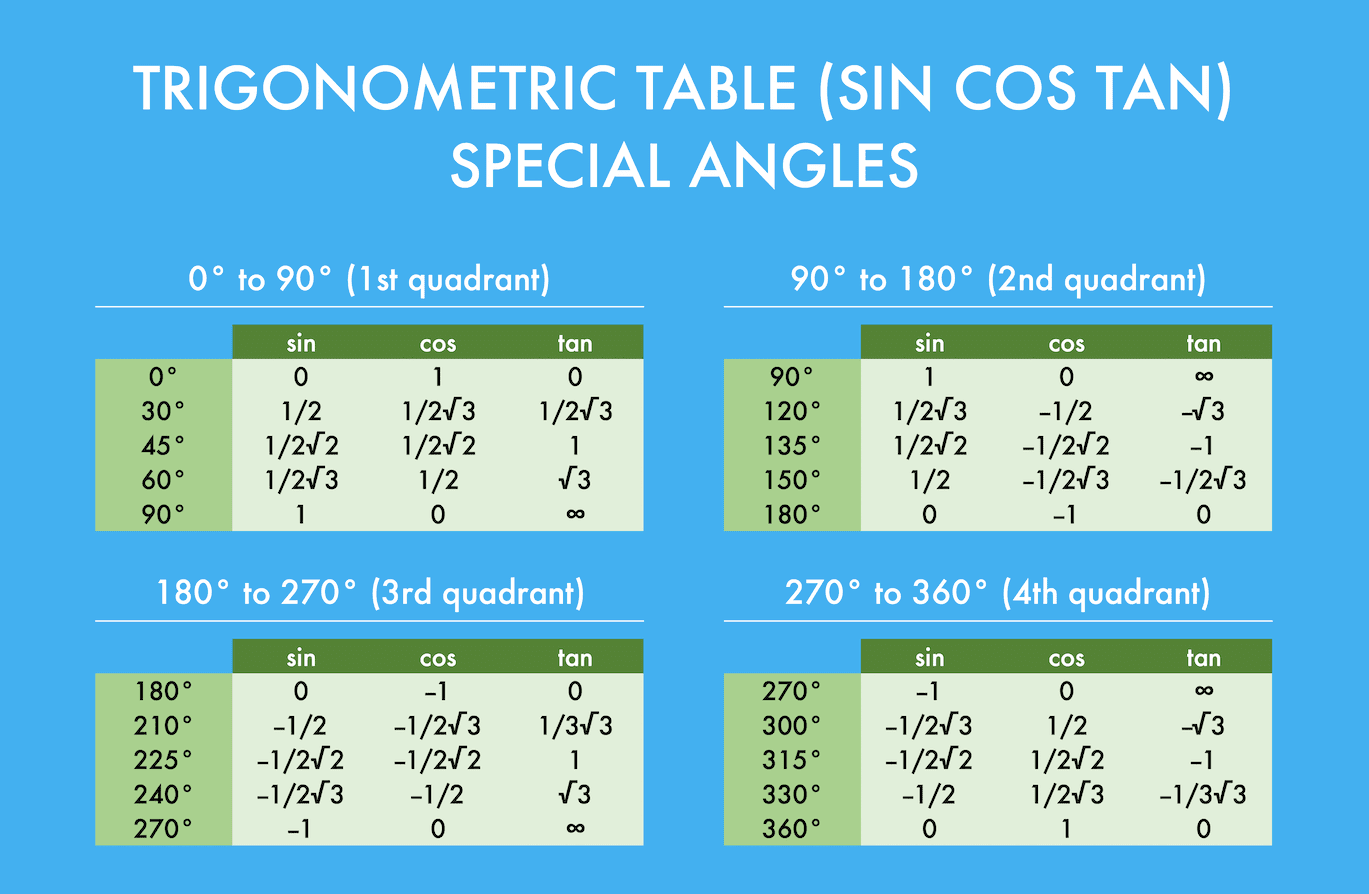



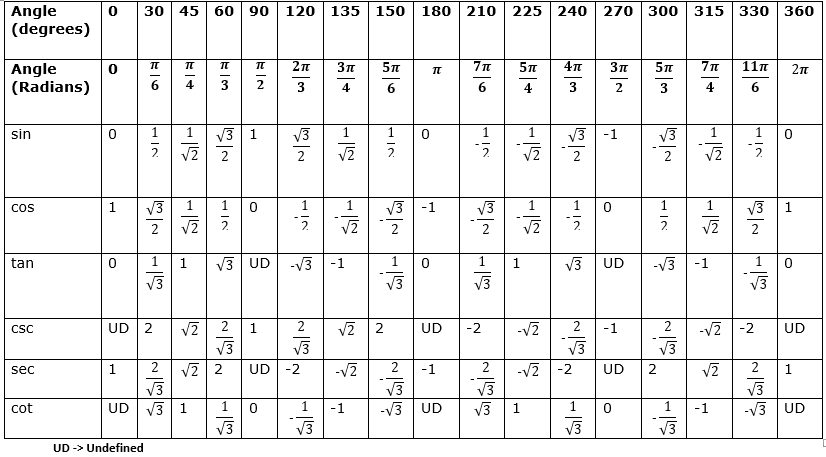
Trigonometric Sin Cos Tan Table 0 360 Degrees Downloadable And How To Learn From It Compute Expert



Exact Trig Values
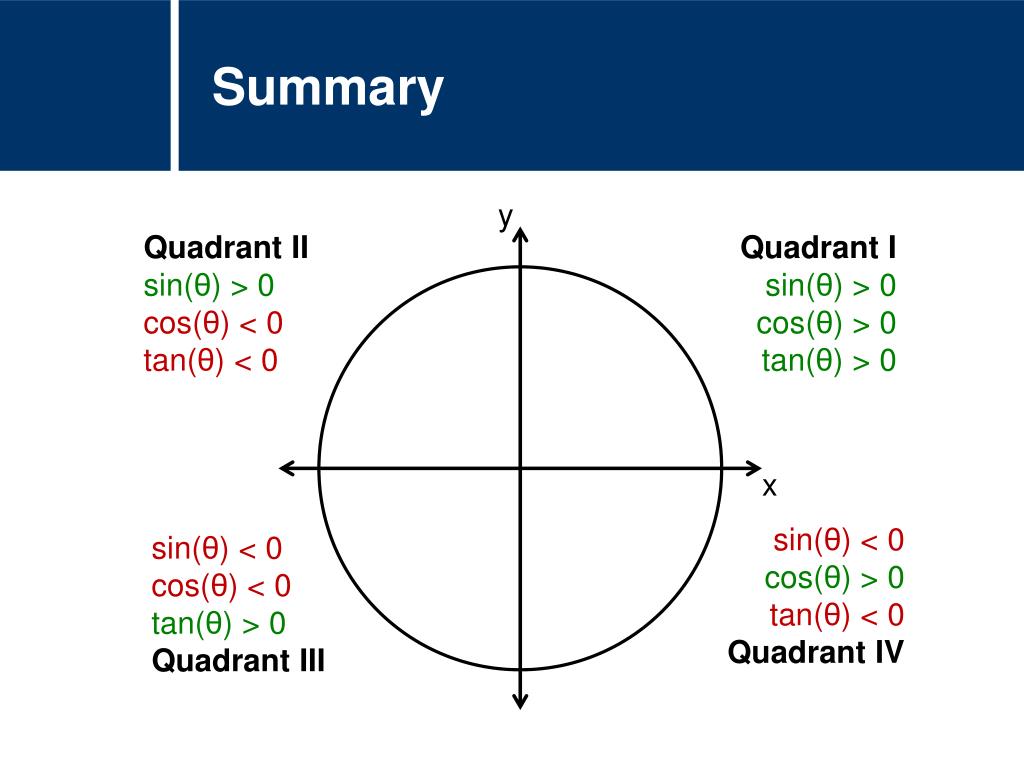



Ppt Mathematics Trigonometry Reference Angles Powerpoint Presentation Id




Chapter 6 Trigonometry Section 6 4 Trigonometric Functions




3 Given Sin U Where U Is In Quadrant 1 And Secv Chegg Com




Sinx 1 4 X In Quadrant Ii Find The Values Of Other Five Trignometric Functions Youtube
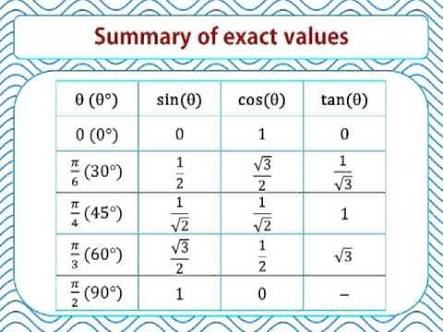



How Do You Express The Value As A Trigonometric Function Of An Angle In Quadrant I Given Csc 330 Circ Socratic




Sine Cosine And Tangent In Four Quadrants




Sine Cosine And Tangent In The Four Quadrants Teachablemath
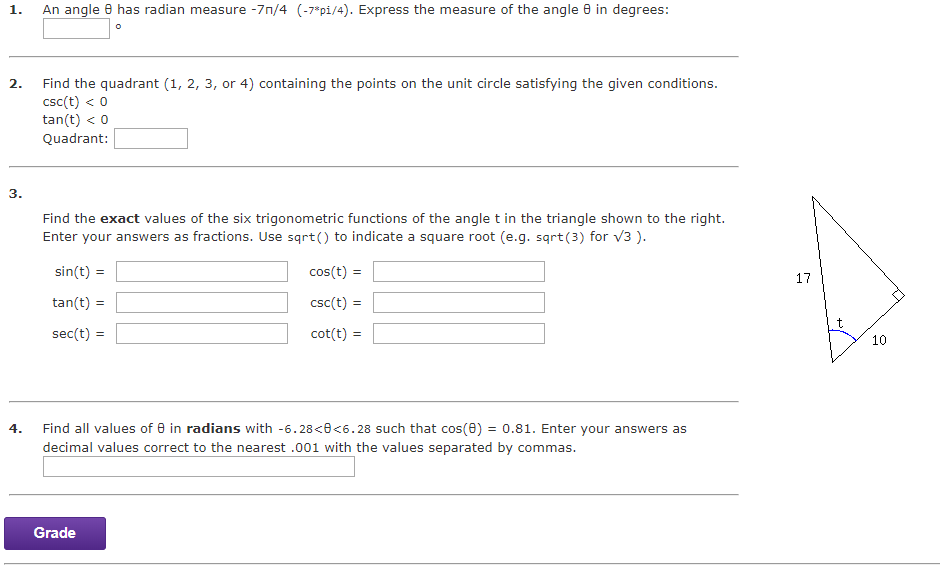



Solved 1 An Angle Has Radian Measure 7n 4 7 Pi 4 Chegg Com
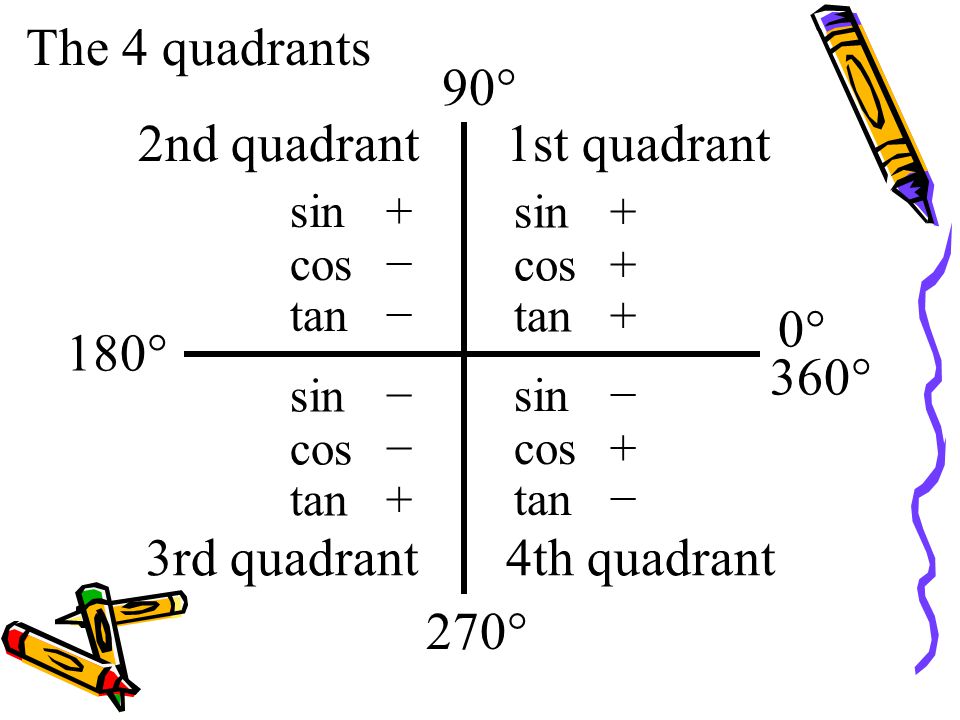



The 4 Quadrants 90 2nd Quadrant 1st Quadrant 0 180 360 Ppt Video Online Download




Cosx 1 3 X In Quadrant Iii Find The Value Of Sinx 2 Cosx 2 Tanx 2
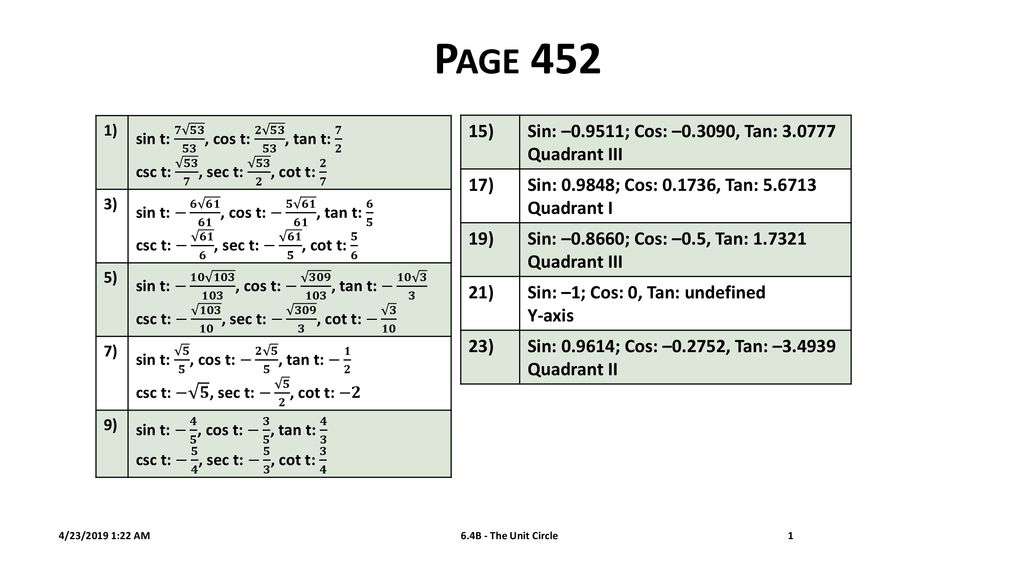



Page Sin 0 9511 Cos 0 3090 Tan Quadrant Iii 17 Ppt Download



If Sin Of Theta Equals 3 8 And Theta Is In Quadrant Ii What Are Cos Tan Csc Cot And Sec Of Theta Socratic




Sine Cosine And Tangent In Four Quadrants




Easy Way Of Memorizing Values Of Sine Cosine And Tangent Mathematics Stack Exchange




Sine Cosine And Tangent In Four Quadrants
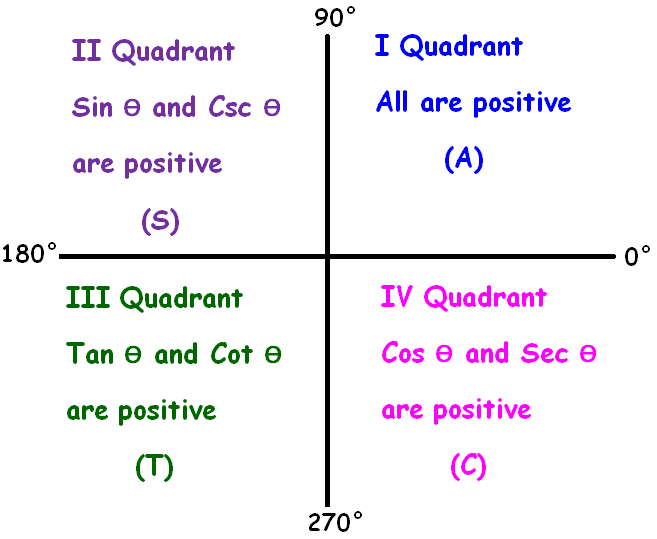



All Sin Tan Cos Rule



1




Trig For Dummies By Adrian P



Signs Of Sin Cos Tan In Different Quadrants Finding Value Of Trign



If Cos X 4 5 Can You Find The Value Of Sin X Quora



Domain Range And Signs Of Trigonometric Functions Ck 12 Foundation




Tanx 4 3 X In Quadrant Ii Find The Value Of Sinx 2 Cosx 2 Tanx 2



Example 6 If Cos X 3 5 X Lies In Third Quadrant Find



How Do You Find The Exact Value Of Cos Theta If Sin Theta 2 3 Socratic
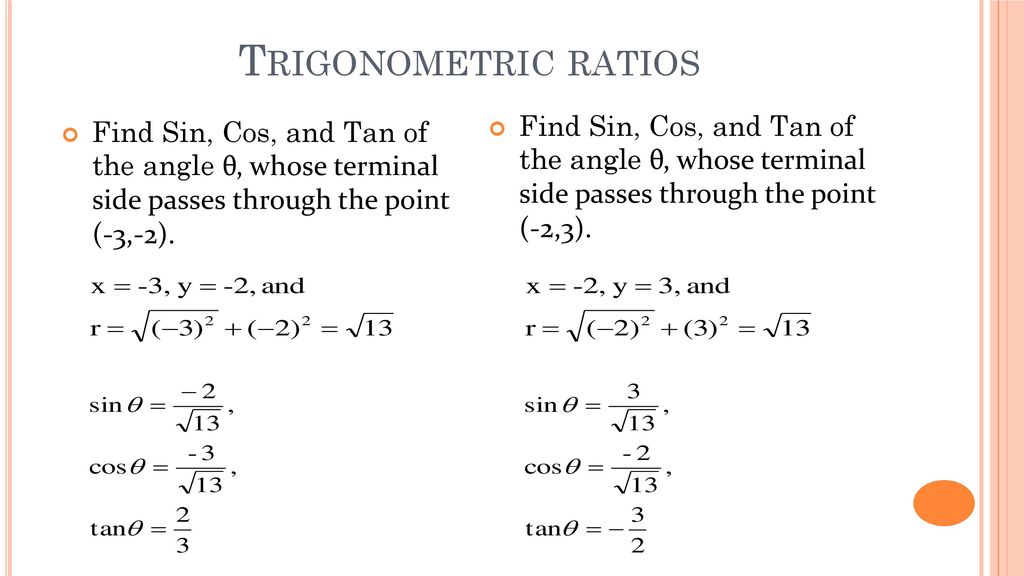



Chapter 6 Trigonometry Ppt Download




Quadrant Plane Geometry Wikipedia




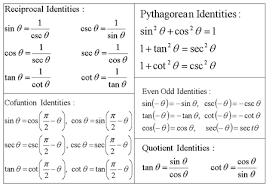
5 1 Fundamental Trig Identities Reciprocal Identities Sin
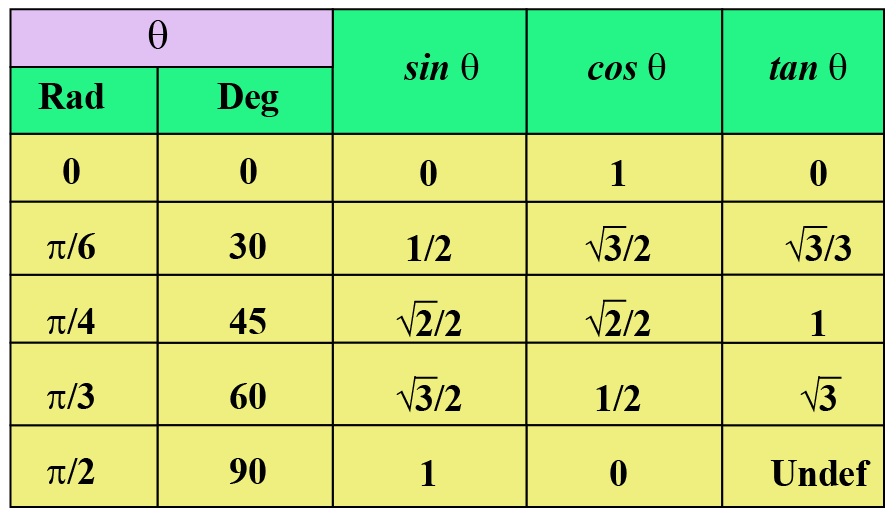



Tangent Function Tan Graph Solved Examples Cuemath



0 件のコメント:
コメントを投稿